62
ONE MORNING, several days after my meeting with Bram and Joel, we were taken to the head office. The head office was only about a quarter of a mile away and was a simple stone structure that resembled our own section. Once there, we were lined up to have our fingerprints taken, which was routine prison service business. But while waiting, I noticed a warder with a camera. After our fingerprints had been taken, the chief warder ordered us to line up for photographs. I motioned to my colleagues not to move, and I addressed the warder: “I would like you to produce the document from the commissioner of prisons authorizing our pictures to be taken.” Photographs of prisoners required such authorization.
It was always valuable to be familiar with regulations, because the warders themselves were often ignorant of them and could be intimidated by one’s superior knowledge. The warder was taken aback by my request and was unable to offer any explanation or produce anything in writing from the commissioner of prisons. He threatened to charge us if we did not consent to have our photographs taken, but I said that if there was no authorization, there would be no pictures, and that is where the matter remained.
As a rule, we objected to having our pictures taken in prison on the grounds that it is generally demeaning to be seen as a prisoner. But there was one photograph I did consent to, the only one I ever agreed to while on Robben Island.
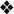
One morning, a few weeks later, the chief warder, instead of handing us hammers for our work in the courtyard, gave us each needles and thread and a pile of worn prison jerseys. We were instructed to repair the garments, but we discovered that most of these jerseys were frayed beyond repair. This struck us as a curious task, and we wondered what had provoked the change. Later that morning, at about eleven o’clock, the front gate swung open, revealing the commanding officer with two men in suits. The commanding officer announced that the two visitors were a reporter and photographer from the Daily Telegraph in London. He related this as if visiting members of the international press were a regular diversion for us.
Although these men were our first official visitors, we regarded them skeptically. Firstly, they were brought in under the auspices of the government, and second, we were aware that the Telegraph was a conservative newspaper unlikely to be sympathetic to our cause. We well knew that there was great concern in the outside world about our situation and that it was in the government’s interest to show that we were not being mistreated.
The two journalists walked slowly around the courtyard, surveying us. We kept our heads down concentrating on our work. After they had made one circuit, one of the guards plucked me by the shoulder and said, “Mandela, come, you will talk now.” In those early days, I often spoke on behalf of my fellow prisoners. The prison service regulations were explicit that each prisoner was permitted to speak only for himself. This was done to negate the power of organization and to neutralize our collective strength. We objected to this role, but made little headway. We were not even permitted to use the word we when we made complaints. But during the first few years, when the authorities needed one prisoner to speak on behalf of others, that individual would be me.
I talked to the reporter, whose name was Mr. Newman, for about twenty minutes, and was candid about both prison and the Rivonia Trial. He was an agreeable fellow, and at the end of our talk, he said he would like the photographer to take my picture. I was reluctant, but in this case relented because I knew the photograph would only be published overseas, and might serve to help our cause if the article was even the least bit friendly. I told him I would agree provided Mr. Sisulu could join me. The image shows the two of us talking in the courtyard about some matter that I can no longer remember. I never saw the article or heard anything about it. The reporters were barely out of sight when the warders removed the jerseys and gave us back our hammers.
The men from the Telegraph were the first of a small stream of visitors during those early months. While the Rivonia Trial still resonated in people’s minds, the government was eager to show the international community that we were being treated properly. There were stories in the press about the inhuman conditions on the island, about how we were being assaulted and tortured. These allegations embarrassed the government, and to combat them they brought in a string of outsiders meant to rebut these critical stories.
We were briefly visited by a British lawyer who had argued for Namibian independence before the World Court, after which we were informed that a Mr. Hynning, a representative of the American Bar Association, would be coming to see us. Americans were then a novelty in South Africa, and I was curious to meet a representative of so august a legal organization.
On the day of Mr. Hynning’s visit we were called into the courtyard. The American arrived in the company of General Steyn, the commissioner of prisons, who rarely made appearances on the island. General Steyn was that unusual thing in the prison service, a polished and sophisticated man. His suits were always of a fine quality and a fashionable cut. He was courtly, and referred to us as “gentlemen,” even doffing his hat to us, something no one else in the prison service ever did. Yet General Steyn oppressed us by omission rather than commission. He basically turned a blind eye to what was happening on the island. His habitual absence emboldened the more brutal prison officials and gave them carte blanche to do whatever they wanted. In his most gracious manner, the general introduced our guest and said, “Gentlemen, please select your spokesman.” A number of the prisoners called out my name.
General Steyn nodded in my direction, and I stood up. In contrast to General Steyn, Mr. Hynning was a heavyset, unkempt man. I thanked him for visiting us and said we were honored by his presence. I then summarized our complaints, beginning with the central and most important one, that we were political prisoners, not criminals, and that we should be treated as such. I enumerated our grievances about the food, our living conditions, and the work detail. But as I was speaking, Mr. Hynning kept interrupting me. When I made a point about the long hours doing mindless work, he declared that as prisoners we had to work and were probably lazy to boot.
When I started to detail the problems with our cells, he interjected that the conditions in backward American prisons were far worse than Robben Island, which was a paradise by comparison. He added that we had been justly convicted and were lucky not to have received the death penalty, which we probably deserved.
Mr. Hynning perspired a great deal and there were those among us who thought he was not altogether sober. He spoke in what I assumed was a southern American accent, and had a curious habit of spitting when he talked, something none of us had ever seen before.
Finally, I had heard enough, and I interrupted him, “No, sir, you misunderstand the points that I am making.” Hynning took offense that I was now contradicting him, while General Steyn watched and listened without comment. Under the circumstances, it was difficult to keep tempers down. The men were angered by Mr. Hynning’s remarks and annoyed that he had been permitted to see us at all. Normally, a visit of any kind lifted our spirits but the visit of Mr. Hynning was demoralizing. Perhaps that is what the authorities wanted. To meet someone with so impressive an affiliation and so little understanding was depressing. Hynning finally just turned and walked away without so much as a good-bye. We were not sorry to see him go.
We discussed Mr. Hynning for years afterward and many of the men imitated the way he spoke to comic effect. We never heard about him again, and he certainly did not win any friends on Robben Island for the American Bar Association.